Data Architect vs Data Scientist: What are the Differences?

Understanding the roles of a data architect vs data scientist is important for anyone considering a career in AI and machine learning.
Data architects focus on designing and managing data frameworks that ensure data integrity and accessibility. In contrast, data scientists analyze complex datasets to extract actionable insights and drive business decisions.
While both roles require a thorough understanding of data management, their functions within an organization are unique.
Both of these positions offer exciting opportunities and play an important part in today's business landscape, yet their responsibilities, required skills, education, and salaries differ significantly.
In this article, we will take a closer look at what these main differences are between a data architect and a data scientist.
But first, did you know that you can find hundreds of open positions in the data science and data architecture field on AI Jobs?
Click here to browse our collection of data-relevant positions at some of the leading tech companies around the globe.
What is a Data Architect?
A data architect is someone who designs and manages the data infrastructure of an organization.
They focus on creating blueprints that outline how data is stored, accessed, and integrated across various systems.
Data architects ensure data integrity, security, and scalability by developing robust data models and frameworks.
The role involves defining data standards and guidelines, as well as selecting appropriate database solutions to support business needs.
By structuring data efficiently, data architects enable easy data flow and accessibility, which is critical for informed decision-making and operational efficiency.
What is a Data Scientist?
A data scientist is a professional who specializes in analyzing and interpreting complex data to help organizations make informed decisions.
They use statistical methods, algorithms, and machine learning techniques to uncover patterns, trends, and insights within large datasets.
By transforming raw data into actionable information, data scientists enable businesses to optimize processes, improve customer experiences, and drive strategic initiatives.
Their main set of expertise lies in the ability to handle vast amounts of data and extract meaningful conclusions that can inform and shape business strategies.
Is a Data Architect the Same as a Data Analyst?
No, a data architect is not the same as a data analyst. While both roles involve working with data, their primary functions and responsibilities differ significantly.
A data architect focuses on designing and managing the data infrastructure, ensuring data is stored and organized efficiently. In contrast, a data analyst primarily works on interpreting and analyzing data to provide actionable insights and support decision-making processes.
Let's take a closer look at some of the main differences between a data architect vs data scientist.
What are the Differences between a Data Architect vs Data Scientist?
Skills
Data architect:
- Proficiency in creating data models that define the structure, relationships, and constraints of data.
- Expertise in managing various database systems, including SQL and NoSQL databases.
- Ability to design complex data architectures that ensure scalability, security, and efficiency.
- Experience with ETL tools and processes to integrate data from multiple sources.
- Familiarity with programming languages like Python, Java, or Scala for scripting and automation.
- Skills in designing and implementing data warehouses to support analytics and reporting.
- Knowledge of data security protocols and compliance requirements to protect sensitive information.
Data scientist:
- Strong foundation in statistical methods to analyze and interpret complex datasets.
- Proficiency in machine learning algorithms and techniques to build predictive models.
- Ability to create visual representations of data insights using tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Matplotlib.
- Advanced skills in programming languages such as Python, R, or SAS for data analysis and modeling.
- Experience with big data frameworks like Hadoop and Spark to handle large datasets.
- Understanding of the specific industry or domain to contextualize data insights effectively.
- Ability to convey complex data findings in a clear, actionable manner to stakeholders.
Responsibilities
Data architect:
- Develop comprehensive data models that dictate the structure, storage, and integration of data.
- Deploy database solutions and ensure they meet organizational requirements for performance and scalability.
- Establish standards and procedures to maintain high data quality and integrity across systems.
- Implement security measures and compliance protocols to protect sensitive data against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Design efficient data flow processes to facilitate seamless data movement and accessibility within the organization.
- Work closely with IT professionals to align data architecture with system infrastructure and business needs.
- Create detailed documentation of data architectures, models, and standards for reference and maintenance.
Data scientist:
- Use statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms to analyze and interpret complex data.
- Build models that forecast trends, behaviors, and outcomes based on historical data.
- Prepare datasets for analysis by identifying and correcting errors, missing values, and inconsistencies.
- Create visualizations to effectively communicate insights and findings to stakeholders using tools like Tableau or Power BI.
- Perform EDA to uncover underlying patterns, correlations, and anomalies in data.
- Partner with business leaders, engineers, and other stakeholders to understand data needs and translate them into actionable insights.
- Maintain thorough documentation of methods, models, and code to ensure reproducibility and transparency in data analysis.
Educational Background
Both data architects and data scientists typically have similar educational backgrounds, usually holding a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, statistics, or a related field.
Advanced degrees, such as a master’s or PhD, in data science, data management, machine learning, or a related discipline are common and can provide a competitive edge.
Specializing in one role over the other, however, requires specific skills that can be acquired through online courses, certifications, and practical experience.
For instance, aspiring data architects might focus on database design, data modeling, and cloud computing, while those aiming to become data scientists would benefit from deepening their expertise in statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization.
Salary
One key difference between a data architect and a data scientist is the salary.
According to ZipRecruiter, a data scientist can earn a median annual salary of about $123,000 in the United States.
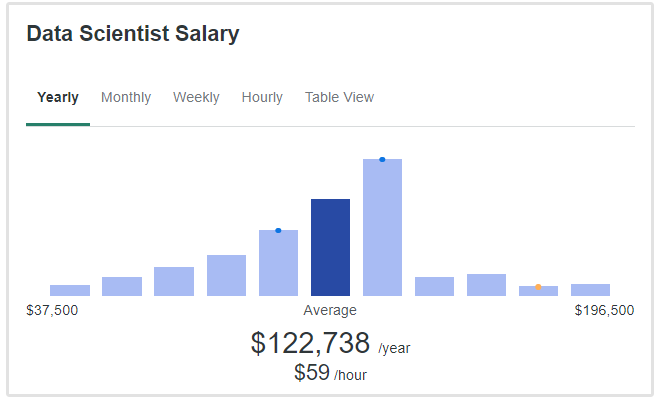
Whereas the median salary for a data architect is $145,000 per annum.
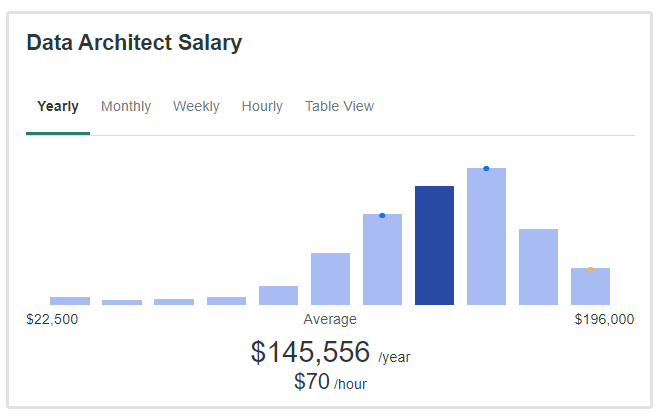
It's important to remember that salaries are dependent on a number of different factors such as location, company, and the candidate's experience.
When evaluating whether you should specialize in data architecture vs data science, don't make your decision based on which role commands the best salary.
Ideally, you should pick the role that you enjoy the most.
Conclusion
While both data architects and data scientists play key roles in using data for business success, their responsibilities and skill sets are distinct.
Data architects focus on designing and managing the data infrastructure, ensuring seamless data flow and security. In contrast, data scientists analyze and interpret data to generate insights that drive strategic decisions.