Research Engineer vs Research Scientist: What’s the Difference?

Are you considering a career in research but unsure about the differences between a research engineer and a research scientist?
Both roles play important parts in advancing technology and knowledge, but their responsibilities, career paths, and educational backgrounds can differ significantly.
In this article, we’ll delve into the key differences between a research engineer vs research scientist. We'll look at their job overviews, salaries, and the educational backgrounds of both roles.
What is the Difference between a Research Scientist and a Research Engineer?
A research scientist is mainly concerned with exploring and understanding fundamental scientific principles.
They conduct experiments and analyze data to develop theories and expand knowledge. Research scientists often work in academic or laboratory settings, pursuing theoretical research that can lead to ground-breaking discoveries.
In contrast, a research engineer focuses on applying scientific principles to solve practical or real-world problems. Their work involves designing, developing, and optimizing systems, processes, or products.
For instance, at the time of writing this post, Tesla is seeking research engineers to develop neural networks for their self-driving platform and other AI technologies.
Research engineers typically work in industries such as technology, automotive, or aerospace, where they create innovative solutions and improvements.
Key Differences:
- Research scientists concentrate on theoretical knowledge and experiments, while research engineers focus on practical applications and technology development.
- Research scientists typically have advanced degrees in scientific fields, while research engineers have degrees in engineering or applied sciences.
- Research scientists aim to advance understanding, whereas research engineers aim to create or improve technologies.
What is a Research Engineer?
A research scientist primarily focuses on conducting experiments and investigations to expand knowledge in a specific field. Their work is often theoretical or experimental, aimed at understanding fundamental principles or discovering new phenomena.
Research scientists typically pursue advanced degrees (Ph.D.) and engage in academic or specialized research to contribute to scientific knowledge.
Their roles involve designing experiments, analyzing data, and publishing findings.
If you're looking for a job as a research engineer or any other engineering field, feel free to check out all of the open job postings on AI Jobs. We've got hundreds of open positions from some of the leading tech companies.
What is a Research Scientist?
A research engineer applies engineering principles to develop practical solutions and technologies. They work on applying scientific research to create new products or improve existing technologies.
Research engineers often have a strong background in engineering disciplines and focus on solving specific technical problems. Their work involves prototyping, testing, and refining technologies to meet industry needs.
They may work in collaboration with research scientists to translate scientific discoveries into practical applications.
Research Engineer vs Research Scientist: Responsibilities
Research Scientist
- Conduct Experiments: Design and perform experiments to test hypotheses and explore new theories.
- Analyze Data: Interpret experimental results using statistical methods and data analysis tools.
- Publish Findings: Write research papers and articles for academic journals to share discoveries with the scientific community.
- Develop Theories: Formulate new theories or models based on experimental data and research findings.
- Collaborate: Work with other scientists and researchers to advance knowledge in specific fields and participate in peer reviews.
Research Engineer
- Develop New Tech: Apply scientific principles to create and improve products, processes, or technologies.
- Prototype and Test: Build prototypes, conduct tests, and refine designs to solve technical problems.
- Apply Engineering Methods: Use engineering methodologies to implement practical solutions based on research findings.
- Document and Report: Prepare technical reports and documentation detailing design processes, test results, and performance metrics.
- Collaborate with Industry: Work with industry partners to translate scientific research into commercially viable products and solutions.
Research Engineer vs Research Scientist: Salary
According to ZipRecruiter, the average salary for a research engineer in the United States is about $106,00 annually, or $51 per hour.
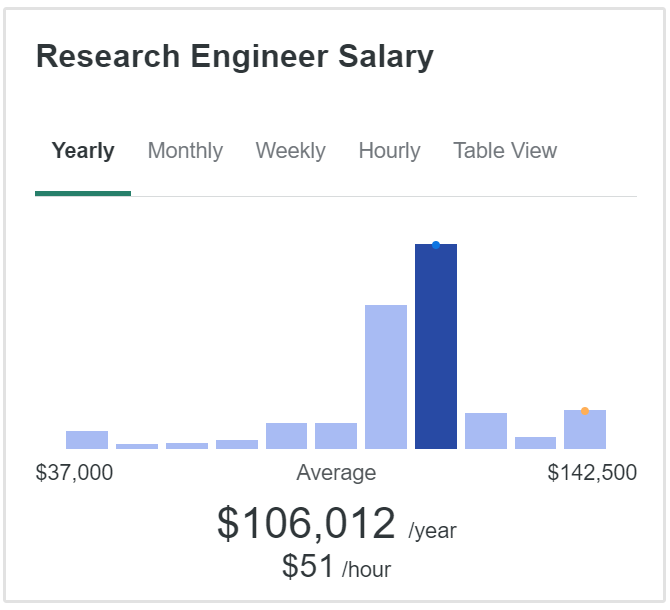
Research scientists on the other hand, can earn up to $130k annualy. (ZipRecruiter)
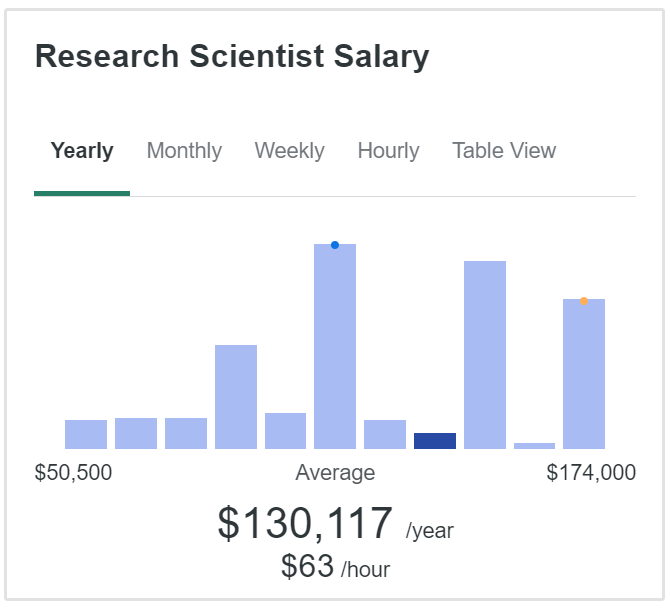
While both roles offer competitive salaries, several factors can influence these figures, including industry, location, experience, and educational background.
For instance, research engineers in high-tech sectors, such as aerospace or software, often command higher salaries than those in academia or less specialized fields.
Likewise, research scientists in pharmaceuticals or biotechnology often enjoy higher salaries due to the specialized knowledge and skills required.
Research Engineer vs Research Scientist: Education
Research Scientist
To become a research scientist, individuals typically need a strong educational background in a specific scientific field. The standard path includes:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A degree in a relevant science discipline (e.g., biology, chemistry, physics).
- Master’s Degree (optional): Some research scientists pursue a master’s degree to gain additional expertise.
- Most research scientists hold a Doctorate in their field, which involves conducting original research and writing a dissertation. Advanced positions and specialized research roles often require a Ph.D.
Research Engineer
Research engineers generally have a background in engineering or applied sciences. The educational requirements usually include:
- Bachelor’s Degree: A degree in engineering (e.g., mechanical, electrical, chemical) or a closely related field.
- Master’s Degree (optional): A master’s degree in engineering or a specialized area can enhance career prospects and expertise.
- For roles involving advanced research or academic positions, a Ph.D. in engineering or a related field may be beneficial, though not always required.
Wrapping Up
Both research scientists and research engineers play important roles in advancing knowledge and innovation within organisations, however, their specific focuses and responsibilities differ quite a bit.
Research scientists are primarily concerned with theoretical exploration and discovery, while research engineers are more focused on applying research findings to real-world problems.
The choice between a career as a research scientist or research engineer depends on your interests, skills, and career goals.
Both roles offer exciting opportunities for intellectual and career growth. By understanding the key differences between these two professions, you can make an informed decision about your future path.