What’s the Difference Between Data Analyst vs Business Analyst

What's the difference between a data analyst and business analyst? Both roles play important parts in organizations, yet they focus on different aspects of data and business processes.
While data analysts dive deep into numbers and trends, business analysts bridge the gap between IT and business to optimize operations and strategies.
In this article, we’ll explore what’s the difference between data analyst vs business analyst, including their job responsibilities, salaries, education requirements, and more.
Whether you're considering a career switch or simply curious, this guide will help clarify the distinctions between these two essential roles.
What is the Difference Between a Data Analyst and Business Analyst?
Data analysts primarily focus on examining and interpreting complex datasets to identify trends and insights, using statistical tools and data visualization. Business analysts, on the other hand, focus on identifying business needs, improving processes, and ensuring that solutions align with business goals.
Now let's take a close look at more detailed differences between data analysts and business analysts regarding the job overview, required skills, salaries, and education.
Data Analyst vs Business Analyst Job Overview
Data Analyst Job Overview
A data analyst is responsible for transforming raw data into actionable insights that help organizations make informed decisions. They gather data from various sources, clean and organize it, and then analyze it to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies.
Data analysts use tools such as SQL, Python, R, and data visualization software like Tableau or Power BI to present their findings in a clear and concise manner.
Their work is critical in driving business decisions across various departments, including marketing, finance, and operations. Data analysts often collaborate with other teams to ensure that the data-driven insights align with the organization’s goals and strategies.
Business Analyst Job Overview
A business analyst focuses on understanding the business’s needs, identifying areas for improvement, and recommending solutions that enhance efficiency and productivity.
Business analysts work closely with stakeholders to gather requirements, analyze business processes, and develop strategies that align with the company’s objectives.
Their role often involves creating detailed documentation, conducting feasibility studies, and ensuring that proposed solutions meet both technical and business needs.
Business analysts must have strong communication and problem-solving skills, as they frequently act as liaisons between management, IT teams, and other departments to ensure successful project implementation.
Data Analyst vs Business Analyst Skills
Data Analyst Skills
Data analysts require a blend of technical and analytical skills to effectively process and interpret complex datasets.
Key skills include:
- Statistical Analysis: Proficiency in using statistical methods to derive meaningful insights from data.
- Programming Languages: Expertise in languages like Python and R for data manipulation and analysis.
- Data Visualization: Ability to use tools such as Tableau, Power BI, and Excel to create clear, impactful data visualizations.
- Analytical Thinking: Strong capability to analyze information, identify patterns, and solve complex problems through data.
- Attention to Detail: Keen eye for detail to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
These skills enable data analysts to provide valuable insights that drive strategic business decisions.
Side note: Are you looking for a job in data analysis or business intelligence? Check out all of the open positions that we've got on AI Jobs.
Business Analyst Skills
Business analysts need a mix of analytical and interpersonal skills to bridge the gap between business needs and IT solutions.
Essential skills include:
- Communication: Excellent verbal and written communication skills to articulate requirements and facilitate effective discussions between stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Strong ability to identify business challenges and propose practical, data-driven solutions.
- Understanding of Business Processes: Deep knowledge of how various business operations function and interact.
- Stakeholder Management: Proficiency in managing relationships with stakeholders to ensure alignment on project goals and requirements.
- Project Management: Skills in planning, executing, and overseeing projects to ensure they meet business objectives.
These skills allow business analysts to enhance organizational processes and drive growth through strategic solutions.
Data Analyst vs Business Analyst Education
Data Analyst Education
Data analysts typically pursue degrees that provide a strong foundation in quantitative and technical skills.
Common educational backgrounds include:
- Bachelor's Degree in Statistics, Mathematics, Computer Science, or Data Science: These programs focus on developing analytical skills and technical expertise necessary for handling and interpreting data.
- Certifications: Many data analysts enhance their qualifications with certifications in data analytics tools and programming languages, such as a Microsoft Certified: Data Analyst Associate or a Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate.
- Courses: Additional courses in areas like machine learning, database management, and cloud computing can further sharpen a data analyst's skill set.
This educational pathway is geared towards equipping individuals with the ability to analyze complex datasets and derive meaningful insights that inform business strategies.
Business Analyst Education
Business analysts often have academic backgrounds that emphasize business and management skills.
Typical educational paths include:
- Bachelor's Degree in Business Administration, Finance, Management Information Systems, or a related field: These programs provide a comprehensive understanding of business operations, financial principles, and organizational dynamics.
- Certifications: Professional certifications like the Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP) or Project Management Institute - Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA) are highly regarded and enhance a business analyst's credentials.
- Courses: Courses in strategic management, process improvement, and stakeholder communication can be beneficial for those seeking to excel in business analysis.
This educational framework is structured to prepare individuals to understand and improve business processes, ensuring alignment between technology solutions and business objectives.
Data Analyst vs Business Analyst Salary
Salaries for data analysts and business analysts can vary significantly depending on factors such as experience, location, industry, and company size. However, both roles generally offer competitive compensation.
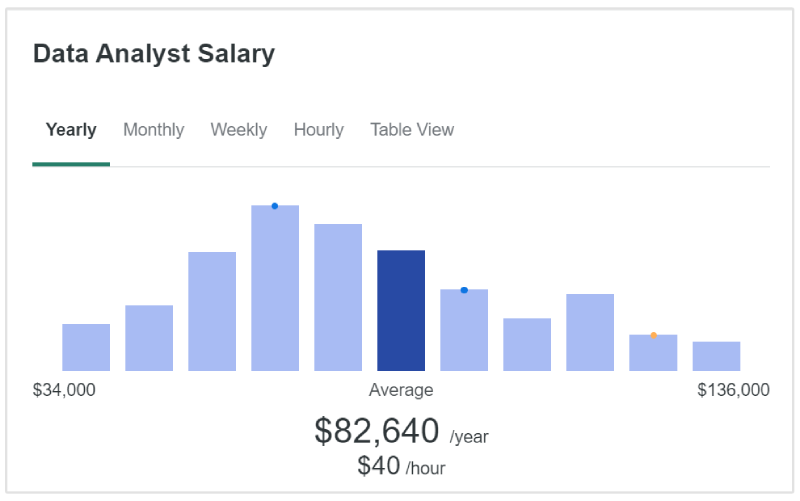
Data analysts typically earn higher salaries due to their specialized technical skills and the increasing demand for data professionals. The median salary for a data analyst in the United States is about $82,000 per year. (ZipRecruiter)
Business analysts also receive competitive salaries, reflecting their strategic role in organizations. The average salary for a business analyst in the United States is about $98,000 per year. (ZipRecruiter)
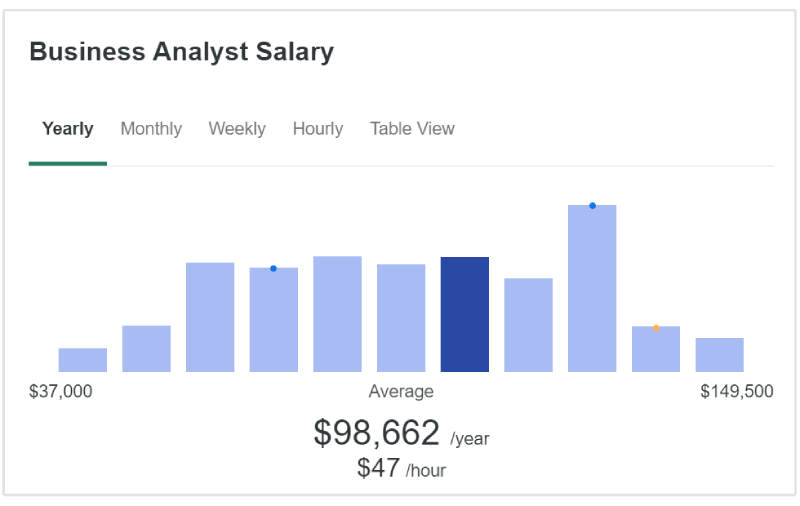
It's important to note that these are average salary ranges, and actual salaries can vary depending on the different factors I mentioned.
Factors such as certifications, industry experience, and the specific company can significantly impact compensation.
Can a Data Analyst Become a Business Analyst?
Yes, a data analyst can certainly become a business analyst. This career transition is quite feasible due to the overlapping skill sets between the two roles.
Data analysts possess strong analytical skills, a keen eye for detail, and the ability to interpret complex datasets—attributes that are highly valuable in business analysis.
Data analysts who are interested in transitioning to a business analyst role will need to develop a broader understanding of business processes, project management, and stakeholder management.
Can You Become a Data Analyst with a Business Degree?
Yes, you can become a data analyst with a business degree. While a technical degree like computer science or statistics is often preferred, a business degree can provide a solid foundation for a career in data analysis.
Business degrees equip individuals with analytical skills, problem-solving abilities, and a strong understanding of business concepts.
These skills are highly valuable in the field of data analysis.
To transition into a data analyst role with a business degree, consider taking additional courses or certifications in:
- Programming languages: Learn languages like Python or R, which are widely used in data analysis.
- Statistics: Gain a solid understanding of statistical concepts and techniques.
- Data visualization: Learn how to create informative charts and graphs to communicate insights effectively.
By supplementing your business degree with these technical skills, you can increase your chances of successfully pursuing a career as a data analyst.
Want to get a job in AI without a degree? Check out our detailed guide on how to start a career in AI without a degree.
Conclusion
Both data analysts and business analytics are crucial to the success of modern businesses but focus on different aspects of data and business processes.
While data analysts dive deep into data to extract insights, business analysts bridge the gap between business needs and IT solutions to drive strategy and efficiency.
Whether you’re drawn to the technical analysis of data or the strategic alignment of business processes, both paths offer rewarding and impactful careers.
With the right skills and education, you can choose the role that best aligns with your strengths and career goals.